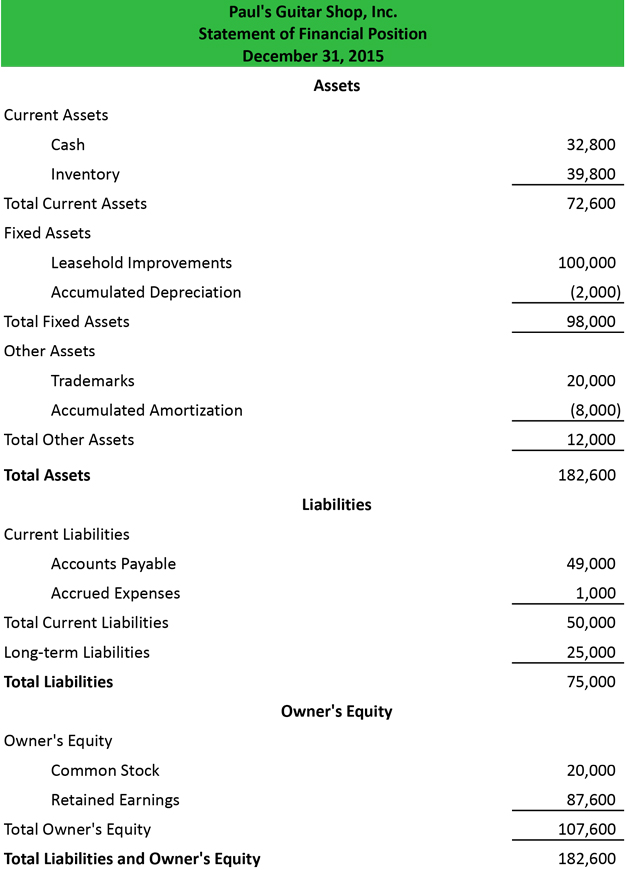

The statement of financial position, often called the balance sheet, is a financial statement that reports the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company on a given date. In other words, it lists the resources, obligations, and ownership details of a company on a specific day. You can think of this like a snapshot of what the company looked like at a certain time in history.
This definition is true in the sense that this statement is a historical report. It only shows the items that were present on the day of the report. This is in contrast with other financial reports like the income statement that presents company activities over a period of time. The statement of financial position only records the company account information on the last day of an accounting period.
In this sense, investors and creditors can go back in time to see what the financial position of a company was on a given date by looking at the balance sheet.
Let’s take a look at a statement of financial position example.

As you can see from our example template, each balance sheet account is listed in the accounting equation order. This organization gives investors and creditors a clean and easy view of the company’s resources, debts, and economic position that can be used for financial analysis purposes.
Investors use this information to compare the company’s current performance with past performance to gauge the growth and health of the business. They also compare this information with other companies’ reports to decide where the opportune place is to invest their money.
Creditors, on the other hand, are not typically concerned with comparing companies in the sense of investment decision-making. They are more concerned with the health of a business and the company’s ability to pay its loan payments. Analyzing the leverage ratios, debt levels, and overall risk of the company gives creditors a good understanding of the risk involving in loaning a company money.
Obviously, internal management also uses the financial position statement to track and improve operations over time.
Now that we know what the purpose of this financial statement is, let’s analyze how this report is formatted in a little more detail.
The statement of financial position is formatted like the accounting equation (assets = liabilities + owner’s equity). Thus, the assets are always listed first.
Assets are resources that the company can use to create goods or provide services and generate revenues. There are many ways to format the assets section, but the most common size balance sheet divides the assets into two sub-categories: current and non-current. The current assets include cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. These resources are typically consumed in the current period or within the next 12 months.
The non-current assets section includes resources with useful lives of more than 12 months. In other words, these assets last longer than one year and can be used to benefit the company beyond the current period. The most common non-current assets include property, plant, and equipment.
Liabilities are debt obligations that the company owes other companies, individuals, or institutions. These range from commercial loans, personal loans, or mortgages. This section is typically split into two main sub-categories to show the difference between obligations that are due in the next 12 months, current liabilities, and obligations that mature in future years, long-term liabilities.
Current debt usually includes accounts payable and accrued expenses. Both of these types of debts typically become due in less than 12 months. The long-term section includes all other debts that mature more than a year into the future like mortgages and long-term notes.
Equity consists of the ownership of the company. In other words, this measures their stake in the company and how much the shareholders or partners actually own. This section is displayed slightly different depending on the type of entity. For example a corporation would list the common stock, preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, treasury stock, and retained earnings. Meanwhile, a partnership would simply list the members’ capital account balances including the current earnings, contributions, and distributions.
In the world of nonprofit accounting, this section of the statement of financial position is called the net assets section because it shows the assets that the organization actually owns after all the debts have been paid off. It’s easier to understand this concept by going back to an accounting equation example. If we rearrange the accounting equation to state equity = assets – liabilities, we can see that the equity of a non-profit is equal to the assets less any outstanding liabilities.
Notice that the balance sheet is always in balance. Just like the accounting equation, the assets must always equal the sum of the liabilities and owner’s equity. This makes sense when you think about it because the company has only three ways of acquiring new assets.
It can use an asset to purchase and a new one (spend cash for something else). It can also take out a loan for a new purchase (take out a mortgage to purchase a building). Lastly, it can take money from the owners for a purchase (sell stock to raise cash for an expansion). All three of these business events follow the accounting equation and the double entry accounting system where both sides of the equation are always in balance.
Accounting & CPA Exam Expert
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.